MEMORY
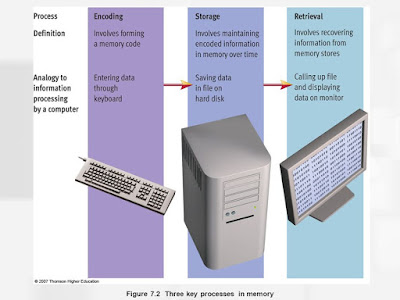
Chapter 5. Our Memory. Since We Obviously Know How It Works. Truthfully though, we never give it much thought, but what is our memory anyway? The inner workings of our memory, is what we’ll talk about today. So, first things first. We all know what memory is for: Memorizing. Or else, why would it be called our ‘memory’? However, how do we ‘memorize’ and ‘remember’? Well, in memory, there are three key processes. The first is Encoding , which involves forming a memory code . It's like the process of recording a video, where you take a video of the event that's happening. Next is Storage , which involves maintaining encoded information in memory over time . So, it means taking that video you recorded and save it in the, well, storage! The final process is Retrieval , which involves recovering information from memory stores . Again, it's just viewing the video from the storage. There is another way to memorize the three key processes in memory. Think of our me...